A woman develops severe PPH after a normal delivery. Bleeding continued despite treatment with oxytocic drugs followed by balloon tamponade.
Examiner – Dr. X
Cadaver
Angled clamp
Aneurysm needle
Needle holder
Vicryl 0/1
Suture scissor and dissecting scissor
Long artery forceps and small swabs
Babcock
Non toothed and catch forceps
6.1 Mention the next procedures you would carry out in the appropriate order. (10 marks)
6.2 Describe in detail and demonstrate how you would perform internal iliac artery ligation. Show how you will apply uterine artery ligation. (70 marks)
6.3 How would you counsel and debrief her. (20 marks)
ANSWERS
6.1(10 marks)
Application of brace sutures
Bilateral Uterine artery ligation
Bilateral Internal iliac artery ligation
6.2 Preliminaries (10 marks)
- Adequate blood transfusion should be continued while the procedure is being carried out.
- Verbal consent should be taken quickly for all possible procedures including blood transfusion, application of brace sutures, devascularisation and hysterectomy.
- Perform a laparotomy under GA
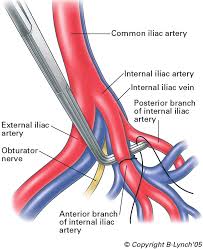
Locating the internal iliac artery. (the candidate should explain and perform where possible) (30 marks, 5 for each point )
- The uterus should be lifted out of the abdominal incision.
- Clamp and divide the round ligament at the midpoint.
- Enter the retroperitoneal space by lifting and snipping the peritoneum of the posterior leaf of the broad ligament at the level of the infundibulo-pelvic ligament.The retroperitoneal space can be bluntly dissected using a moist gauze swab placed on a long artery forceps.
- The bifurcation of the common iliac artery, the internal iliac artery and the external iliac artery can be seen and the arterial pulsations can be palpated.
- The ureter can be seen crossing the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. It can be identified as a cord like structure with peristalsis.Identify the ureter and gently push it further medially.
- The internal iliac artery is the more medial vessel seen between the external iliac artery and the ureter. It can be differentiated from the vein by its colour and the pulsations.
Ligating the artery (30 marks. 5 for each point)
- It is ligated 3–4 cm away from the bifurcation.
- A right angled clamp is passed under the artery from lateral to medial to avoid damage to the adjacent veins which is the greatest danger of this procedure.
- The artery is ligated using a double strand of absorbable suture material which is fed into the right angled clamp. Repeat the procedure on the opposite side.
- The dorsalis pedis pulse should be felt and saturation should be checked with a pulse oxymeter.
- Bleeding should subside before the abdomen is closed after placing a drain.
- The woman should be closely monitored in an ICU. Document all details of the procedure
6.3 Debriefing -20 marks
- Explain the reason for the PPH
- Mention the team involved
- Explain the management from the beginning
- Mention the final management
- As the uterus is in situ warn that it may recur in the next pregnancy.
- Inform her Hb level and the need to take iron for about 3 months
- Inform that complete recovery will occur in about 2 weeks.
- Advise to attend the clinic in two weeks.
- Inform regarding family planning for at least 2 years






